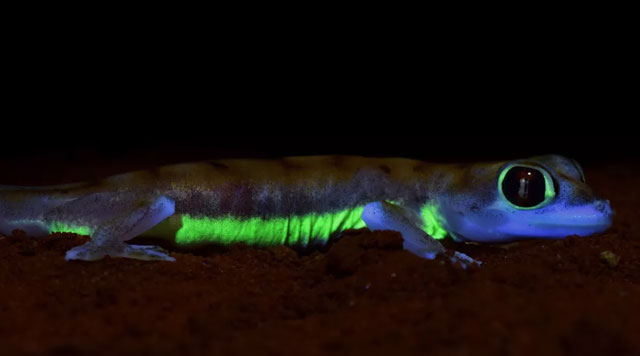
Scientists have just discovered that the Namibian Desert Gecko has bright spots in the dark, neon green glow under the moonlight.
This mechanism of light generation has never been seen before in terrestrial vertebrates.
The Palmetto Gecko (Pachydactylus rangei) has translucent skin with large yellow markings: stripes on the sides and a ring around the eyes. But these areas light up when they absorb the bluer light of the moon.
Fluorescence has been found in other reptiles and amphibians, either through their bones or through chemical secretions on their skin. Palmetto geckos, however, have membranes that produce their lumen with the help of pigmented skin cells filled with guanine crystals. These cells, called iridophores, were previously associated with color rendering in geckos and lizards, but this is the first evidence that they also allow geckos to glow in the dark.
The palmetto gecko is approximately 4 to 6 inches long. These geckos use wide webbed legs to traverse fine sand and are mainly active at night.
In 2018, the study authors found that chameleons had shiny bones through their skin. Study co-author Mark Scherz, from the University of Potsdam, Germany, said the discovery prompted scientists to search for light hidden in other reptiles and amphibians.
David Prötzel, the lead author of this study in Munich, raised the Palmetto gecko in his home and made a surprising discovery of bright UV lights on his geckos.
The researchers then examined 55 samples of the Palmetto gecko under UV light, and they found evidence of fluorescence in both male and female geckos.
“In fact, it turns out that many other species, including geckos, have skin transparent enough to see the fluorescence of their bones under strong UV light,” Scherz said.
 Yellowish yellow bands on the sides of the gecko are visible to other geckos, but are hidden from predators that attack from above.
Yellowish yellow bands on the sides of the gecko are visible to other geckos, but are hidden from predators that attack from above.
But in the Palmetto gecko, a bright neon green light comes from the keratinocytes. Although iridophores were not previously associated with gecko fluorescence, they are known to fluoresce in some species of coral reef fish. The Palmetto Gecko is the first known gecko to have two types of epidermal cells. There is a luminescent type and a non-luminescent type.
The light these cells produce brighter than the light emitted by chameleon bones and is one of the brightest examples of fluorescence in land animals, the study authors said.
Such bright signs along the lower body and around the eyes would be highly visible to other geckos, but would be obscured by predators with higher vantage points, such as owls. or jackal.
Although scientists are not sure how most animals use their fluorescence, the location and brightness of these markers, as well as their visibility in the dry desert environment. The gecko, where there is not much vegetation, suggests that fluorescence plays a role in the gecko’s social interactions.
“We have observed that in captivity, although these animals are largely solitary, they always run close to each other to greet each other after a short separation. They also lick the vapor that remains on top of each other. So there are many reasons for being able to see each other at a long distance that would be very helpful for these geckos, ”Scherz said.