On this day, 60 years ago, October 4, 1957, the Soviet Union successfully launched the Sputnik 1 satellite into space, opening the race to conquer global space and opening new skies for them. Human being.
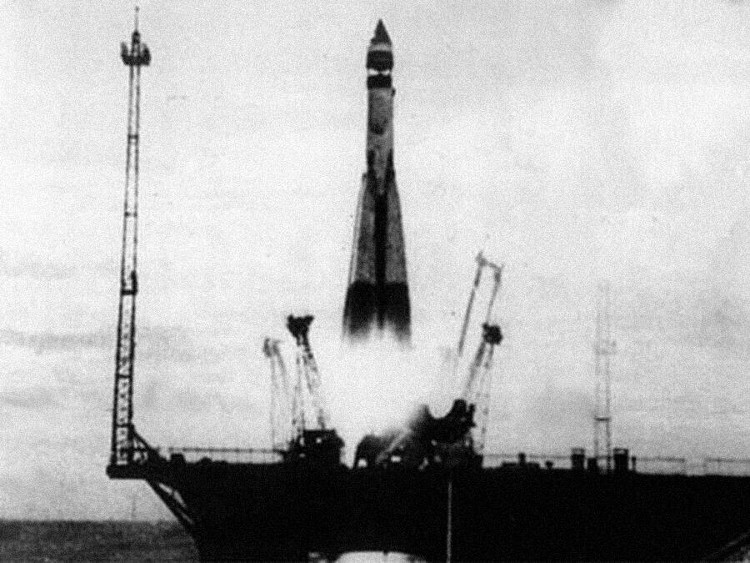 The R-7 boosters leave the ground, carrying the first man-made satellite into space.
The R-7 boosters leave the ground, carrying the first man-made satellite into space.
Sputnik 1, the bearer of humanity’s desire to conquer the universe, has been successfully launched …
The person who leads the way in the age of space conquest
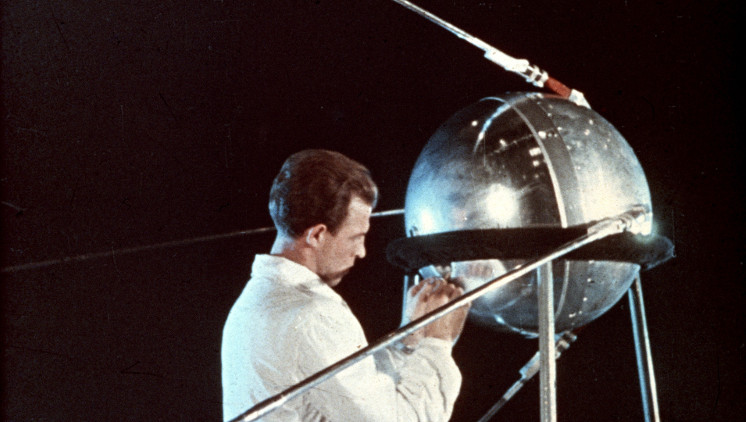
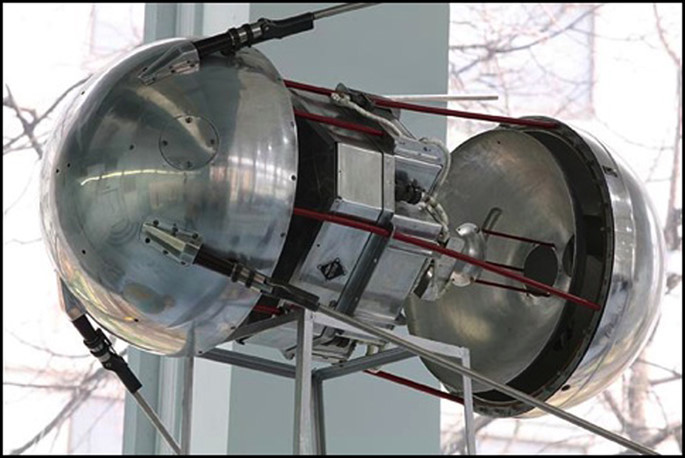
The private museum of the Russian rocket and space company RSC Energia is the place to keep the “treasures” of the Soviet space conquest. Several models for the first flight of Sputnik 1 are still kept here. These models have a very special shape that everyone can immediately think of as Sputnik 1. It is a small metallic sphere weighing a little over 80 kg; the surface is polished and several antennas are mounted.
A Soviet engineer was editing the last detail of the Sputkik 1 in the fall of 1957, before putting it into space.
Astronaut Alexander Kaléry – responsible for flight control at RSC Energia, remembers: Despite its simple design, the world’s first satellite performed extremely efficiently.
“It was inspired by the first successful launch of the R7 rocket. The design goal of Sputnik 1 is to be as simple as possible, without the need for sophisticated scientific equipment. It only includes a thermometer, a battery.” Modular and Air-Powered – This allows the Soviet Union to win over the United States in its race to become the first nation to launch a satellite off Earth. ”
M. Igor Komarov, directeur général de l’Agence fédérale de l’aérospatiale russe de Roscosmos, a déclaré: “C’est vraiment important pour tout le peuple soviétique. Parce qu’il s’agit d’une avancée importante, en est la preuve. Pour l’avancement de la technologie, le succès des programmes a été réalisée par l’ingénieur en chef Sergey Korolev et les principaux scientifiques de l’Union soviétique. Ensemble, ils ont créé une nouvelle industrie dans le monde: l’industrie spatiale industrielle ».
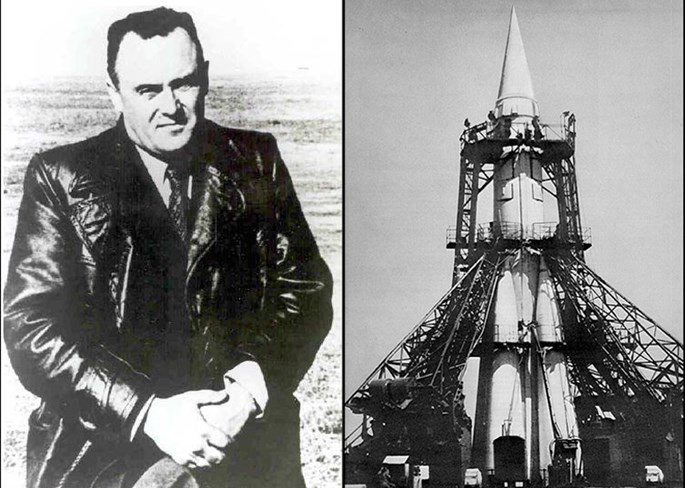 Chief Project Engineer Sergei Korolev and an upgraded R-7 missile launcher to put Sputnik into orbit.
Chief Project Engineer Sergei Korolev and an upgraded R-7 missile launcher to put Sputnik into orbit.
The shocking world event 60 years ago
Roger-Maurice Bonnet, former chief scientist of the European Space Agency ESA, recalls: “It was a huge event, the start of the Soviet space conquest that nobody expected. We thought America was the first to launch this race at the time. This created a great crisis in Washington because they did not expect the Soviet Union to be able to perform such miracles ”.
“People often misinterpret the importance of Sputnik when they think of it as just an ordinary satellite. The subject here is the rocket that helped put Sputnik into space. ‘an intercontinental ballistic missile developed by the Soviet Union and which operated successfully on the first test.] the first in American history was appalled at the power of the Soviet Union.
Back then, with the space race underway, Soviet chief engineer and director of space Sergei Korolev quickly started a new race. Less than a month after the release of Sputnik 1, Sputnik 2 launched with Laika on 03/11/1957. Laika became the first living creature to enter space, although it was set on fire on its historic journey.
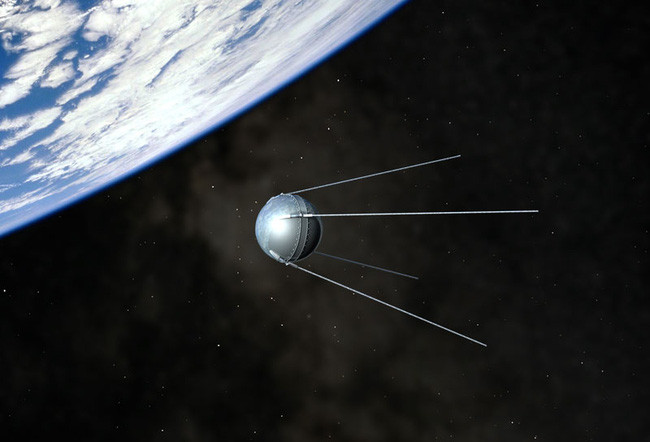 An image of Sputnik 1’s activities in space.
An image of Sputnik 1’s activities in space.
Glorious and ambitious past
Sharing with the Euronews news agency, astronaut Alexei Leonov, who was the first to walk in space, recounted his memories: “Sergei Pavlovich Korolev installed a manned spaceship with rockets. Vostok, the new version of Sputnik rocket launchers, they issued a rule on the recruitment of crews for spacecraft from among people working as jet pilots. in the first test group “.
According to astronaut Alexander Kalery, the Soviet plan was in place in the late 1950s when the government enacted a future space exploration program. In this shot, they refer to lunar autopilot stations, flights to Mars and Venus, human flights to space, “they’re talking about men walking on Mars, Venus, Moon and building space stations there.

Less than a month after the release of Sputnik 1, Sputnik 2 was launched with the dog Laika.
The fact that the Soviet Union set foot in space initially panicked America because it realized it was “inferior in missile technology.”
After a series of failed launches, the first American satellite, Explorer 1, was finally launched on January 31, 1958.
So far, the Soviet Union has achieved a great ideological victory by putting the dog Laika into space orbit on Sputnik 2.
Between the end of the 1950s and the beginning of the 1960s, Soviet space programs successively obtained a series of first names, such as: The first man to fly in space; The first woman to fly in space; The first three men flew into space; First spacewalk, first spacecraft to approach the Moon; The first spacecraft to orbit the Moon; the first spacecraft near Venus; and the first soft landing on Mars.
However, the “game” changed when the United States took a huge leap forward in the late 1960s, with the Apollo program culminating with the historic moon landing on July 20, 1969.
Is the halo extinguished?
The Soviet Union began the space age six decades ago with the launch of Sputnik 1, and paved the way for humans to enter space after putting astronaut Yuri Gagarin into orbit near Earth on December 12. April 4, 1961.
However, the country, once a pioneer in space exploration, is now struggling to restore its position after a long brain drain and budget cuts.
After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, post-Soviet Russia was unable to launch a spacecraft on any planet in the solar system, including the moon. During this time, US probes traveled to the most remote regions of the solar system. Even new countries entering the space sector like India, China, and Japan have sent unmanned ships to the Moon and beyond.
A report by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development of the OECD at the end of last year showed that the budget for the Russian space exploration race in 2013 was only about 5.3 billion. USD, much less than for America and even the “laggard” of China.
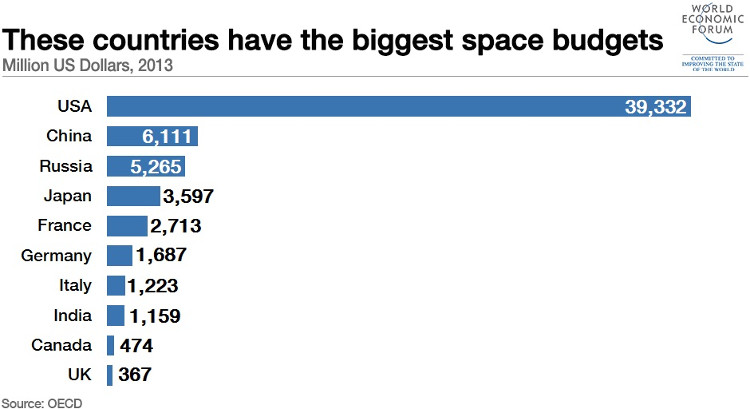
Le budget du programme spatial russe en 2013 était d’un peu plus de 5 milliards de dollars, tandis que celui des États-Unis et de la Chine était de 39 et 6 milliards, respectivement.
Le monde a fait exploser une nouvelle race dans le travail d’occupation de l’espace. Non seulement de nouveaux visages comme l’Inde, la Chine et plus récemment l’Australie, mais aussi la présence de grandes entreprises comme Space X du milliardaire Elon Musk ou le patron de Blue Origin of Amazon Jeff Bezos.
What do Russians today know about the history of Sputnik?
The Euronews reporter interviewed visitors to the Moscow Astronautical Museum and received the following responses:
“The only thing I know is that the Soviet Union launched Sputnik into space in 1957,” one teenager said.
“The Russians put a lot of effort into achieving this feat. And this is a very important thing for the history of the world, ”said a tourist.
“I learned it at school. Now I bring my children here so they can learn more about the heroic history of the Russians. It is our pride that we were the first to explore the universe, ”said one of the dads enthusiastically.
 This heritage continues to this day. All the astronauts used the Baikonur space airport to board the international space station ISS as Sputnik 1. The Russian Federal Aerospace Agency in Roscosmos also had many new projects as a partner. Among them are the project of cooperation with NASA to build a space station around the Moon in the period 2024-2026, or the project of the Russia-Europe interplanetary station project, to explore the red planet.
This heritage continues to this day. All the astronauts used the Baikonur space airport to board the international space station ISS as Sputnik 1. The Russian Federal Aerospace Agency in Roscosmos also had many new projects as a partner. Among them are the project of cooperation with NASA to build a space station around the Moon in the period 2024-2026, or the project of the Russia-Europe interplanetary station project, to explore the red planet.
“I believe being the first in this field is no longer important. What matters is what we work for together. These are incredibly important groundbreaking discoveries. In addition, we are also actively preparing to build a space station on the Moon in 2020. so that we can better understand the environment here, maybe even get closer to our goal. building houses on the Moon “- said Komarov, director of Roscosmos.
On s’attend à ce que de tels projets sur la Lune et sur Mars fassent l’exploit de ce que Spoutnik, un projet ambitieux et extrêmement réussi jusqu’à 60 ans plus tard, a créé.


