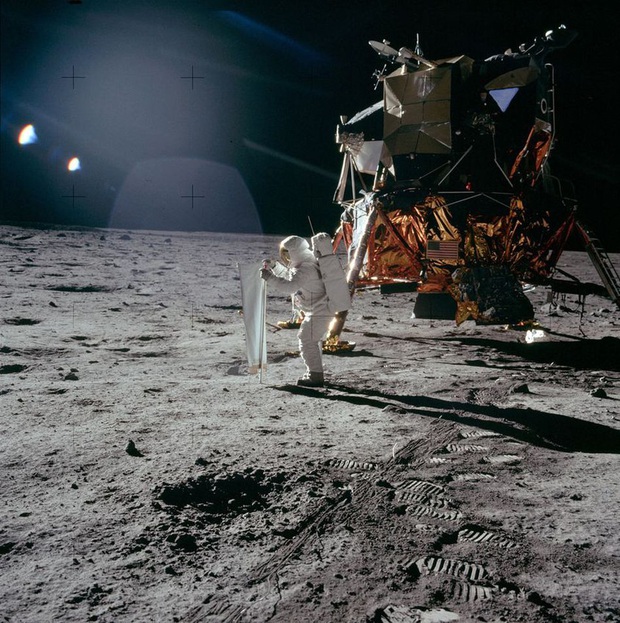
The footprints left by the astronauts of the Apollo moon mission will likely last for at least 100 million years.
Looking at the starry sky at night, what do you often think of? Are we really alone in this universe? After all, where is the limit of the universe?
The truth is, the vast space outside of our planet contains many secrets that science has yet to know. But on the contrary, there are also some interesting surprises that after thousands of years of research in astronomy, people have used their intelligence to observe, reason and draw.
What are the most surprising things you can say to yourself while looking at the night sky?
1. Neutron stars can rotate at a speed of 600 rpm
When a star reaches its neutron star stage, it has reached one of the last points on its evolutionary planet. These massive stars were born in supernova explosions, but they collapse in their core by a radial gravitational force and then spin extremely quickly due to the physics of this process.
Normally, neutron stars can spin up to 60 revolutions per second after birth. But in a particular case, this speed can be increased to more than 600 rpm.
2. Cosmic space is completely silent
In order for sound waves to reach your ears and bounce off your eardrum, you need a medium to propagate. But since there is no air in the empty space of the universe, there is still an appallingly strange silence there.
In contrast, on Earth there is an atmosphere and atmospheric pressure that allows sound to travel. This explains why there is so much noise on the ground.
3. The number of stars in the universe is countless
Basically, we don’t know exactly how many stars there are in the universe. But scientists can use estimates to answer the question: How many stars are there in our galaxy, the Milky Way? They then multiplied that number with their best prediction about the number of galaxies in the universe.
After all these calculations, NASA can only say with certainty that the number of stars in this universe is so high that it cannot be counted.
A study by the Australian National University estimates that there are 70 billion million stars in the universe.
4. The footprints left by astronauts during the Apollo moon mission will probably last at least 100 million years.
The moon has no atmosphere, wind, or water to wash away or wash away the characteristics of Apollo astronauts. This means that the footprints, the traces of rover wheels, the traces left by human spaceships will be kept on the moon for a very long time.
The only thing that can blur these traces is the deposit of cosmic dust sucked up on the lunar surface. These are “micrometric meteors” that continually attack the Moon, but this process will be very slow.
5. The Sun represents 99% of the mass of the solar system
Our star, the Sun, is so dense that it represents 99% of the mass of the entire solar system. Mass is what allows the Sun to rule over all the planets, attracting them.
Technically, our Sun is a G-type main sequence star, which means that every second it fuses around 600 million tonnes of hydrogen with helium. It also converts around 4 million tonnes of material into energy as a by-product.
When the Sun dies, it will become a red giant, bulging and engulfing the Earth and everything on it. But don’t worry: it won’t happen in 5 billion years.
6. The total solar energy falling to Earth per hour is more than the total energy the planet uses for a year.
Over the past century and a half, people have increasingly harnessed solar energy to serve their lives. According to the Yale Environment Journal 360 Degree, in 2017 the entire world increased its solar capacity by 30%, which is equivalent to 98.9 gigawatts of solar power that was produced.
Even so, this amount of electricity is only 0.7% of the world’s annual electricity consumption.
7. If two pieces of metal of the same element touch each other in space, they will self-bond and stay together forever.
This amazing effect is known as cold soldering. This happens because the atoms at the two edges of the two pure (undoped) metal fragments no longer distinguish their place. Therefore, these atoms automatically bind to neighboring atoms, belonging to neighboring metal fragments, causing them to stick together.
Interestingly, cold welding never occurs in the Earth’s atmosphere, as there are always water and air molecules separating the two metal fragments, no matter how close they are.
The cold welding that occurs in the aerospace industry is an effect that has many implications for the construction and repair of spacecraft and the future of the vacuum construction industry.
8. The largest asteroid in our solar system is a giant space rock called Ceres.
The asteroid of Ceres – sometimes called a dwarf planet – is about 950 km in diameter. So far, Ceres is known to be the largest asteroid in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. It alone occupies a third of the mass of the belt. The area of Ceres is approximately the area of India or Argentina.
There is a human spaceship that approached and flew around Ceres, helping us unravel its mysteries. Dawn, or Dawn, was launched into space in 2007 and took eight years to reach Ceres.
9. A day on Venus is longer than a year on Earth
Venus is extremely slow on its axis, taking approximately 243 days on Earth to complete an entire cycle. Ironically, a year on Venus is shorter than a period around its own axis. Venus only takes 226 Earth days to orbit the Sun.
If you live on Venus, you will see the Sun rise every 117 Earth days. This means that the Sun will only rise twice in the year of Venus. Also, since Venus rotates clockwise, the Sun will rise in the west and set in the east.
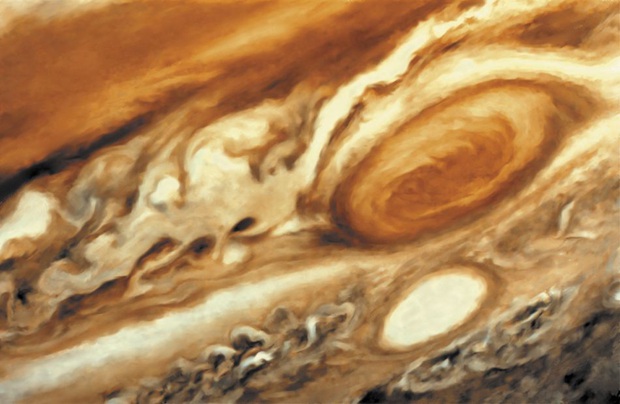
10. Jupiter’s big red spot is shrinking
The giant storm above Jupiter, visible through telescopes from Earth as a large, shrinking red spot. With a diameter of nearly 11 times that of Earth, Jupiter can have storms devouring all three Earths in its belly. The Great Red Spot was once such a storm, but so far its size has shrunk to only a third.
11. One of Saturn’s moons has two distinct tones
Iapetus, one of Saturn’s 62 moons, is in fact a very unique celestial body. A moon has two very distinct tones, with one side much darker than the other. This feature does not appear on any other moon in the solar system.
The color of Iapetus must be related to its position relative to the rest of Saturn’s moons. Iapetus is outside of Saturn’s belt and as a result, it suffers from a lot of space debris being thrown to the surface, darkening its color on one side.
12. The position of the North Star will change
It will be strange that the North Star is no longer the North Star. But over the next 13,000 years, scientists predict it will happen. In case you didn’t know, the Earth’s axis has undergone a movement called “precession,” which means it will slowly tilt to draw a cone, like a spinning top when it’s about to fall. .
When this happens, the North Star’s biased position relative to Earth will shift, leaving it more stationary in the northern hemisphere night sky. Then we will have a new North Star.